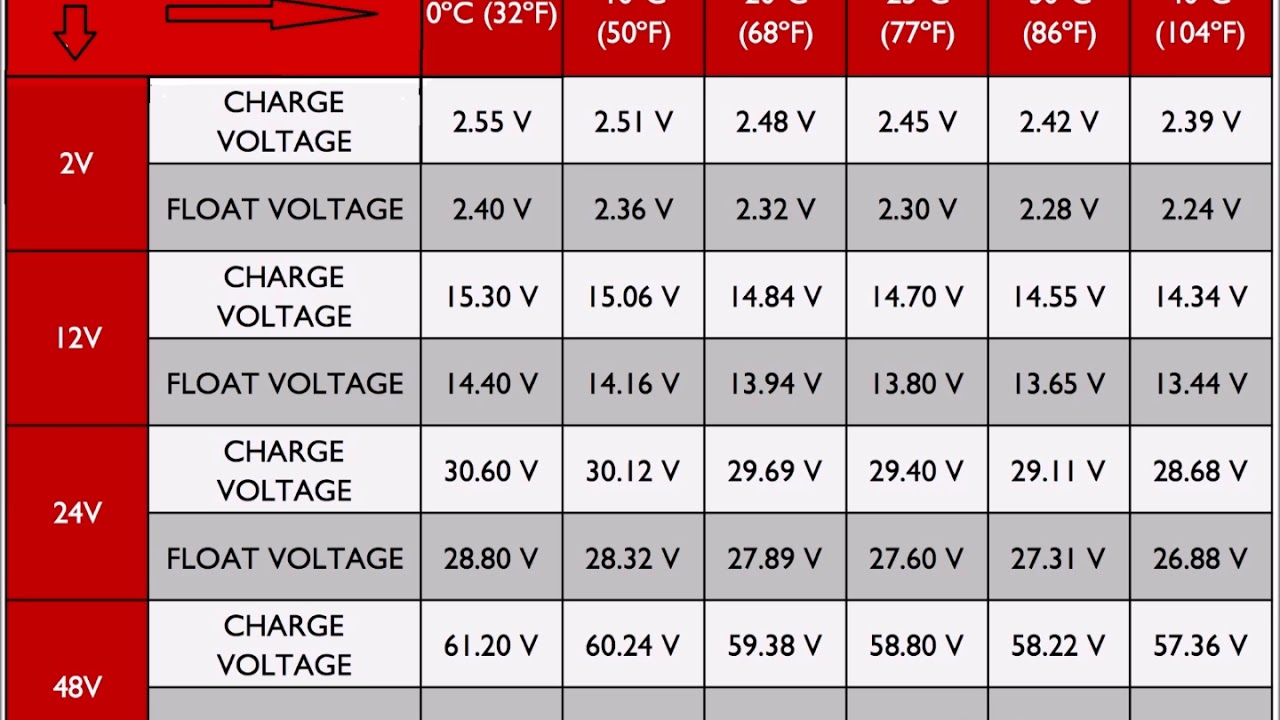
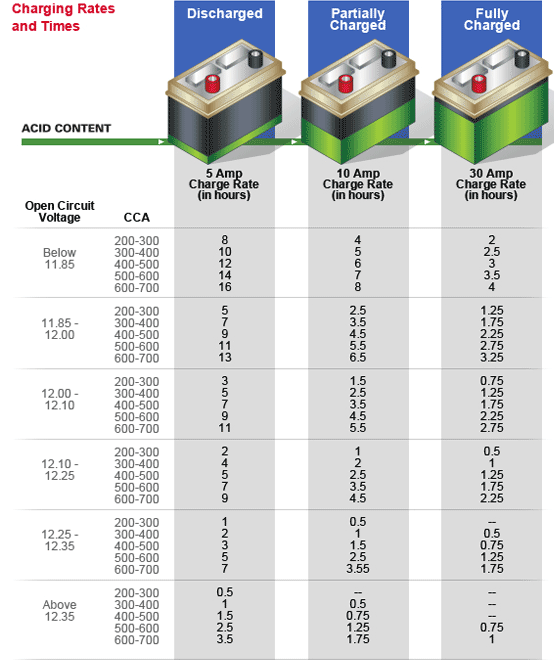
Ever found yourself stranded with a dead battery, wondering if letting your car idle could have saved the day? It's a common question: will my car battery charge at idle? The simple answer is…it's complicated. While your engine running does generate power, several factors determine whether that power is enough to effectively replenish a drained or weak battery.
Understanding the nuances of car battery charging while idling is crucial for every driver. It's about more than just getting your car started; it's about understanding your vehicle's electrical system and avoiding future headaches (and potential towing bills). So, let's delve into the mechanics of idle charging and separate fact from fiction.
Essentially, when your car is running, the alternator generates electricity to power the car's electrical systems, including the headlights, radio, and importantly, recharging the battery. But, at idle, the alternator spins slower, producing less power. This lower output might be enough to maintain the battery’s current charge and power essential systems, but is it sufficient to recharge a significantly depleted battery? That's where things get tricky.
The history of car battery charging is intertwined with the evolution of automobiles themselves. Early vehicles relied on magnetos for ignition, but as electrical systems became more complex, the need for a reliable power source like the lead-acid battery emerged. Similarly, the alternator replaced the less efficient generator, improving the car's ability to replenish its battery while running. Today, with the rise of electric vehicles, charging methods are again evolving, but for traditional combustion engine cars, understanding alternator-based charging remains essential.
The core issue with idle charging is the limited power output of the alternator at low RPM. While idling might sustain a healthy battery, it often provides insufficient current to effectively recharge a depleted one. This is especially true in modern cars with numerous electrical demands, like heated seats, advanced infotainment systems, and climate control, all drawing power even when the car isn't moving.
If your battery is severely depleted, idling is unlikely to fully recharge it in a reasonable timeframe. Consider jump-starting your car and then driving it for a sustained period at higher RPMs to allow the alternator to generate sufficient charging power.
Benefits of Driving versus Idling for Charging:
1. Faster Charging: Driving at higher RPM spins the alternator faster, resulting in a much quicker and more effective charge compared to idling.
2. Complete Recharge: Driving ensures your battery receives a full charge, prolonging its lifespan and preventing future starting issues.
3. Reduced Strain on the Alternator: Prolonged idling to charge a deeply depleted battery can put excessive strain on the alternator, potentially shortening its life.
Action Plan for a Dead Battery:
1. Jump-start the car.
2. Drive for at least 30-60 minutes at moderate speeds (above 2000 RPM) to allow the alternator to recharge the battery.
3. Have your battery and alternator tested to ensure they are functioning correctly.Advantages and Disadvantages of Idle Charging
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Maintains existing charge if battery is healthy | Inefficient for recharging a depleted battery |
| Can provide temporary power to accessories | Can waste fuel and contribute to emissions |
Best Practices:
1. Regularly check your battery's voltage.
2. Limit the use of power-hungry accessories while idling.
3. Avoid short trips that don’t give the alternator enough time to recharge the battery.
4. Have your charging system inspected annually.
5. Consider a battery trickle charger for maintaining the battery during periods of infrequent use.FAQs:
1. Will my car battery charge at idle with the lights on? - It might maintain the charge or very slowly charge if the battery is healthy, but it’s inefficient for a depleted battery.
2. How long should I idle my car to charge the battery? - Idling is not recommended for charging a depleted battery. Drive instead.
3. Can idling damage my car battery? - Prolonged idling can strain the alternator.
4. How can I tell if my alternator is charging the battery? - Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage while the engine is running.
5. Is it bad to leave my car idling for a long time? - Yes, it wastes fuel, contributes to pollution, and can potentially cause engine wear.
6. What are signs of a bad alternator? - Dimming headlights, flickering interior lights, and difficulty starting.
7. How can I maximize the life of my car battery? - Avoid extreme temperatures, limit short trips, and regularly check the charging system.
8. What should I do if my car battery keeps dying? - Have your battery and alternator tested.Tips and Tricks: Carry jumper cables in your car for emergencies. Use a battery tender during long periods of storage.
In conclusion, understanding whether your car battery will charge at idle is more nuanced than a simple yes or no. While idling can maintain a healthy battery's charge, it's generally insufficient to revive a dead one. Driving at moderate speeds for a sustained period is the most effective way to recharge your car battery. Recognizing the factors that influence charging, understanding the limitations of idle charging, and practicing proper battery maintenance are essential for every driver. By taking proactive steps to care for your battery, you can avoid unexpected breakdowns, extend the life of your battery and alternator, and enjoy countless miles of worry-free driving. Remember to prioritize driving over idling for charging, get your battery and alternator checked regularly, and equip yourself with the knowledge and tools necessary to keep your vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly.
Unlocking top paying trades your path to a secure future
Jefferson county jail phone number staying connected
Mastering pixel art full body characters a comprehensive guide