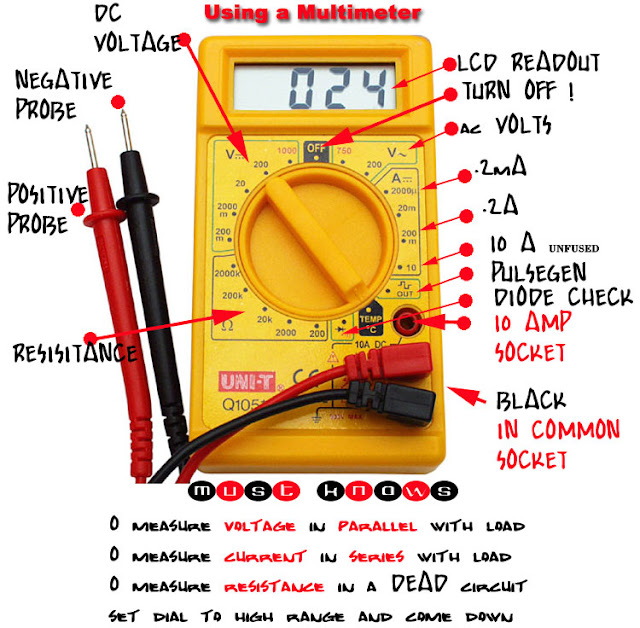
Ever stared at your multimeter, puzzled by the squiggly line? That, my friend, is the AC current symbol, your gateway to measuring the flow of alternating current. This seemingly simple symbol unlocks a world of electrical understanding, allowing you to troubleshoot circuits, diagnose appliance issues, and delve into the dynamic world of electricity. This article will demystify the AC current symbol on your multimeter, guiding you from basic identification to advanced measurement techniques.
The AC current symbol, often represented as a tilde (~) or a sinusoidal wave, signifies the fluctuating nature of alternating current. Unlike direct current (DC), which flows consistently in one direction, AC periodically reverses its direction. This back-and-forth flow is the foundation of most household electricity, powering everything from your lights to your laptop. Understanding how to measure this fluctuating current is crucial for any aspiring electrician or DIY enthusiast.
Multimeters, those handy handheld devices, are essential tools for measuring various electrical properties, including voltage, resistance, and of course, current. They provide a window into the electrical world, allowing you to quantify the invisible flow of electrons. When working with AC circuits, selecting the correct setting on your multimeter, indicated by the AC current symbol, is paramount for accurate and safe measurements.
The importance of correctly interpreting and utilizing the AC current symbol on your multimeter cannot be overstated. Misinterpreting the symbols or selecting the wrong settings can lead to inaccurate readings, damaged equipment, or even personal injury. Therefore, taking the time to understand the nuances of AC current measurement is a worthwhile investment for anyone working with electrical systems.
While seemingly straightforward, measuring AC current with a multimeter can present challenges. One common issue is overloading the multimeter, which can occur if the current being measured exceeds the meter's capacity. This can damage the device and potentially create a hazardous situation. Another challenge is ensuring proper connection to the circuit. Incorrect placement of the multimeter probes can lead to inaccurate readings or even short circuits. Therefore, understanding the proper techniques and safety precautions is essential for successful AC current measurements.
The AC current symbol (~) differentiates AC measurements from DC measurements which are often indicated by a straight line with a dashed line beneath it or a single straight line. Most digital multimeters will automatically display the measured value in Amperes (A) or milliamperes (mA).
Three key benefits of understanding the AC current symbol are:
1. Accurate Measurements: Correctly identifying and using the AC setting ensures precise current readings, essential for diagnosing electrical issues.
2. Safety: Selecting the appropriate AC current range prevents overloading the multimeter and protects both the user and the equipment.
3. Troubleshooting: Accurate AC current measurements are crucial for identifying faulty components or wiring in electrical circuits.
Action Plan for Measuring AC Current:
1. Select the AC current setting on your multimeter (indicated by the ~ symbol).
2. Choose the appropriate current range. Start with a higher range and reduce if necessary to obtain a more precise reading.
3. Turn off the power to the circuit being measured.
4. Connect the multimeter probes in series with the circuit.
5. Turn the power back on and observe the reading.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Multimeter for AC Current Measurement
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Versatile and can measure various electrical parameters. | Can be damaged by overload if incorrect range is selected. |
| Relatively inexpensive and readily available. | Requires some technical knowledge to use effectively. |
| Portable and easy to use in various locations. | May not be as accurate as specialized current measuring devices. |
FAQs
1. What does the AC current symbol look like? It's typically a tilde (~) or a sinusoidal wave.
2. What unit is AC current measured in? Amperes (A).
3. Why is it important to select the correct current range? To avoid overloading the multimeter.
4. What happens if I measure AC current on the DC setting? You may get an inaccurate reading or damage the meter.
5. Can I measure AC current in a live circuit? Yes, but with extreme caution and proper safety measures.
6. What are some common issues when measuring AC current? Overloading the meter, incorrect probe placement.
7. What are some safety tips for measuring AC current? Always turn off the power before connecting the meter, use insulated probes, and wear appropriate safety gear.
8. Where can I find more information on using a multimeter? Online tutorials, user manuals, and electronics textbooks.
In conclusion, understanding the AC current symbol on your multimeter is paramount for anyone working with electrical circuits. From diagnosing faulty appliances to ensuring accurate measurements, the ability to measure AC current effectively is a valuable skill. By following the outlined steps, understanding the potential challenges, and adhering to safety guidelines, you can confidently navigate the world of AC current measurement and unlock the full potential of your multimeter. Mastering this fundamental skill empowers you to tackle electrical projects with confidence and precision, whether you're a seasoned electrician or a curious DIY enthusiast. So, embrace the squiggly line, explore the power of your multimeter, and embark on your journey of electrical discovery.
Winning contracts demystifying the award letter and its power
Conquer boat seat mildew the ultimate guide
Achieve a stunning stone finish with paint