Ever wondered how Uncle Sam determines salaries for its massive workforce? The federal government's pay system, a complex structure of grades and steps, dictates the compensation for millions of employees. This system isn’t arbitrary; it’s a carefully constructed framework designed to ensure fair and consistent compensation across various roles and responsibilities.
Navigating the intricacies of federal pay grades and steps can feel like deciphering a complex code. This system, however, is crucial for both employees and the government. For employees, understanding the system is key to understanding their earning potential and career progression. For the government, the structured system provides a standardized approach to compensation, promoting transparency and equity in how taxpayer dollars are spent.
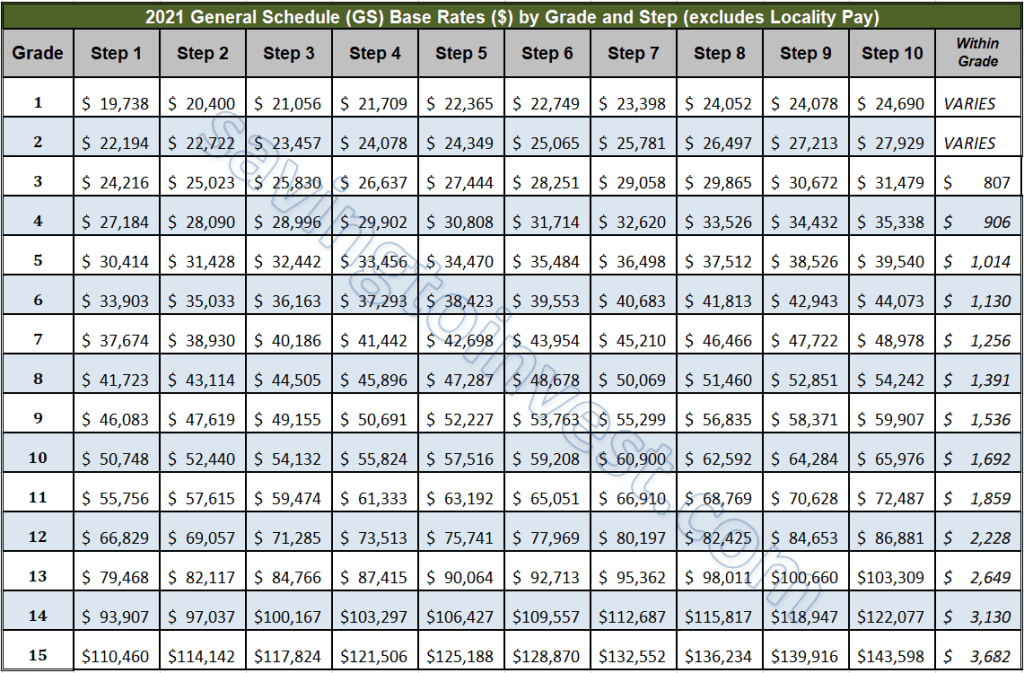
At the heart of this system lies the General Schedule (GS) pay scale. This scale divides positions into 15 grades (GS-1 to GS-15), each representing a different level of complexity, responsibility, and required qualifications. Within each grade are ten steps, representing incremental increases in pay within that grade. An employee typically progresses through the steps based on time in service and performance.
Beyond the basic GS grades and steps, additional factors influence an employee's final salary. Locality pay adjustments account for variations in the cost of living across different geographic areas. Special pay rates may also apply to certain positions requiring unique skills or located in hazardous duty zones. Unpacking these elements is crucial to grasping the full picture of federal compensation.
The federal pay system has its roots in the Classification Act of 1923, aiming to standardize civil service positions and salaries. Over time, this system has evolved to reflect changing economic realities and workforce needs. Today, the system faces challenges like attracting and retaining top talent in a competitive job market and ensuring pay equity across diverse occupations.
The federal government pay structure offers several advantages. The structured system provides clear career progression paths and predictable salary increases. It also aims to create a fair and transparent compensation system, minimizing discrepancies based on factors unrelated to job performance. The GS system promotes stability and encourages long-term government service.
To understand your potential salary, you'll need to identify the GS grade and step associated with a specific position. This information is typically included in job announcements. You can then refer to the official OPM (Office of Personnel Management) pay tables to determine the base salary. Factor in locality pay adjustments for a more accurate estimate of your potential earnings in a specific location.
A potential career progression plan within the federal government might involve starting at a lower GS grade and progressing to higher grades through experience, further education, and demonstrated competence. For example, an employee might begin at GS-7, progress to GS-9 after a few years, and eventually reach GS-12 with additional experience and qualifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Federal Government Pay Grades and Steps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Structured Career Progression | Limited Negotiation Power |
| Pay Transparency and Equity | Salary Compression at Higher Grades |
| Job Security and Benefits | Slow Progression Through Steps |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a GS grade? A GS grade represents the level of complexity and responsibility of a federal job.
2. How do I advance through steps? Step increases are typically based on time in service and satisfactory performance.
3. What is locality pay? Locality pay adjusts salaries based on the cost of living in a specific geographic area.
4. Where can I find the official pay tables? The official pay tables are published by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM).
5. How are special pay rates determined? Special pay rates are established for positions with unique requirements or located in hazardous areas.
6. How does the federal pay system compare to the private sector? Federal pay is generally competitive with the private sector, especially when considering benefits.
7. How can I learn more about federal government career paths? Explore resources on the USAJOBS website and the OPM website.
8. What are some tips for negotiating salary in a federal job? While negotiation is limited, highlighting your skills and experience can help secure a higher starting step within a grade.
One helpful tip is to use online salary calculators that factor in locality pay. This provides a more realistic estimate of your potential take-home pay.
In conclusion, the federal government pay system, built upon grades and steps, offers a structured approach to compensation, aiming to balance fairness, transparency, and efficiency. Understanding the complexities of this system is essential for anyone considering or currently pursuing a federal career. While the system has its advantages, such as clearly defined career paths and a focus on pay equity, challenges such as salary compression and limited negotiation power remain. By familiarizing yourself with the intricacies of federal pay grades and steps, you can effectively navigate your career path and maximize your earning potential within the federal government. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, advocate for your worth, and contribute to the vital work performed by the federal workforce. Exploring available resources, understanding the progression system, and staying informed about updates to the pay tables are crucial for success in navigating the federal pay landscape. Ultimately, mastering the federal pay system is not just about understanding your paycheck; it's about understanding the value and structure of your contribution to public service.
Unlocking victory nike hypervenom phantom 3 black gold review
Capricorn and taurus compatibility a celestial love story
Victorias secret evening dresses a closer look