White, the seemingly simplest of colors, holds a surprisingly complex digital life. From the crispness of a blank webpage to the subtle glow of an e-reader, achieving "white" on screen requires more than meets the eye. This journey into the world of white color codes will uncover the hidden depths of this ubiquitous shade.
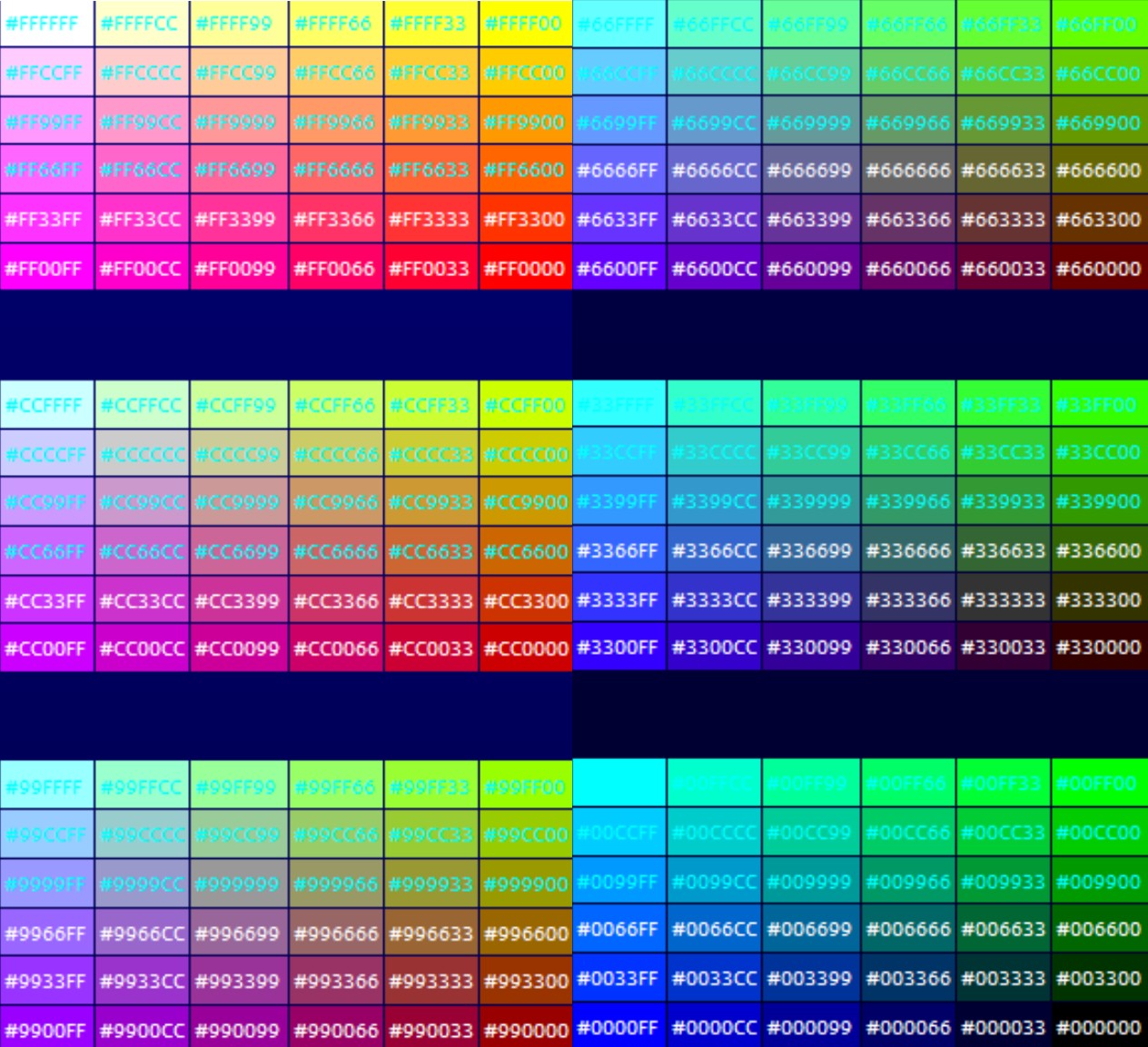
What exactly do we mean by "white color codes"? Simply put, these are the numerical representations that tell a computer or digital device how to display white. These codes, often expressed in hexadecimal, RGB, or other formats, are the building blocks of digital color, dictating how white appears across various platforms and displays.
Think of it like a secret language for screens. Just as a painter mixes pigments to create white on canvas, digital designers and developers use these codes to blend red, green, and blue light to achieve the desired white on screen. The variations within these codes allow for subtle adjustments, influencing the perceived "whiteness" and its interaction with surrounding colors.
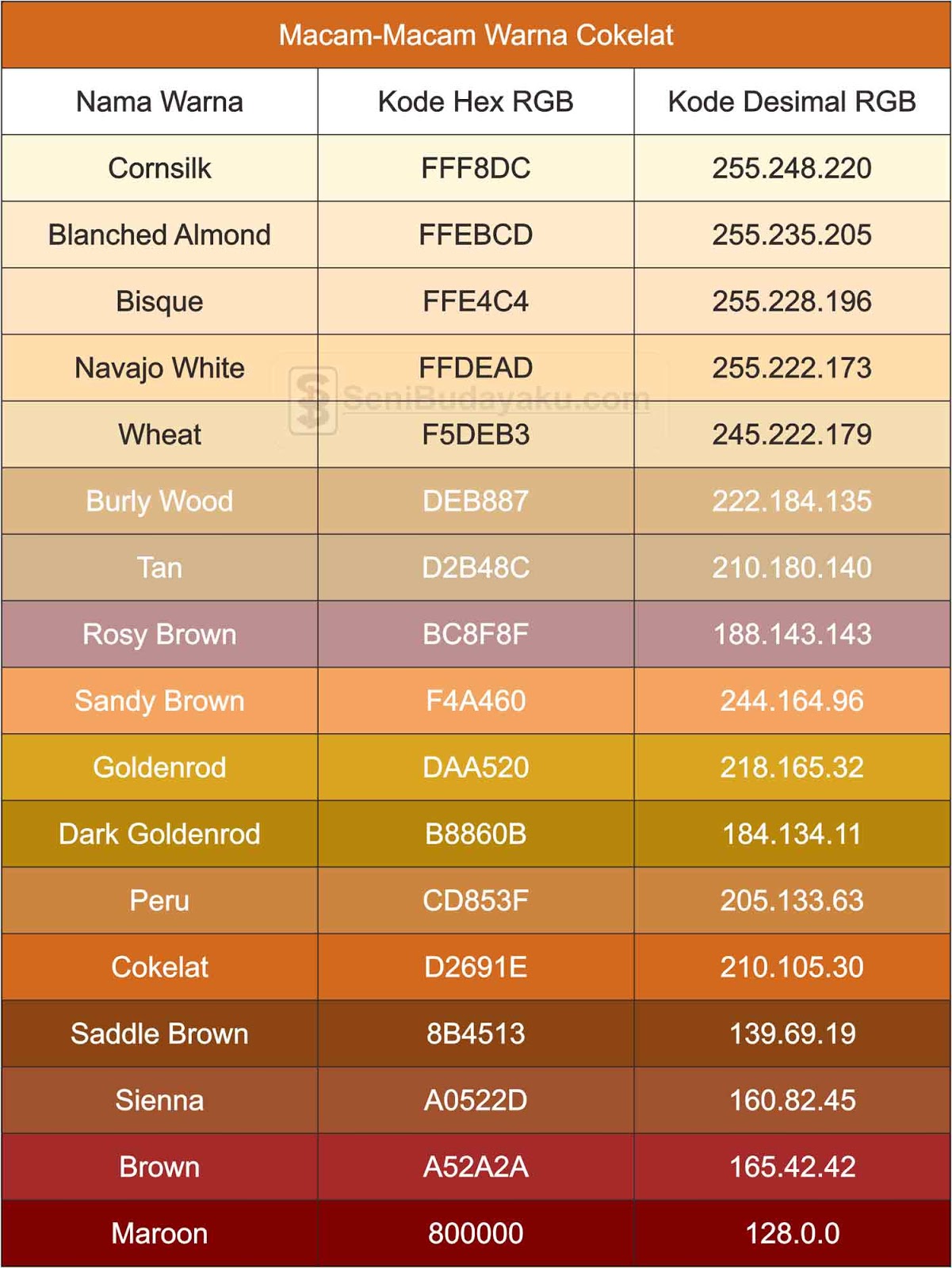
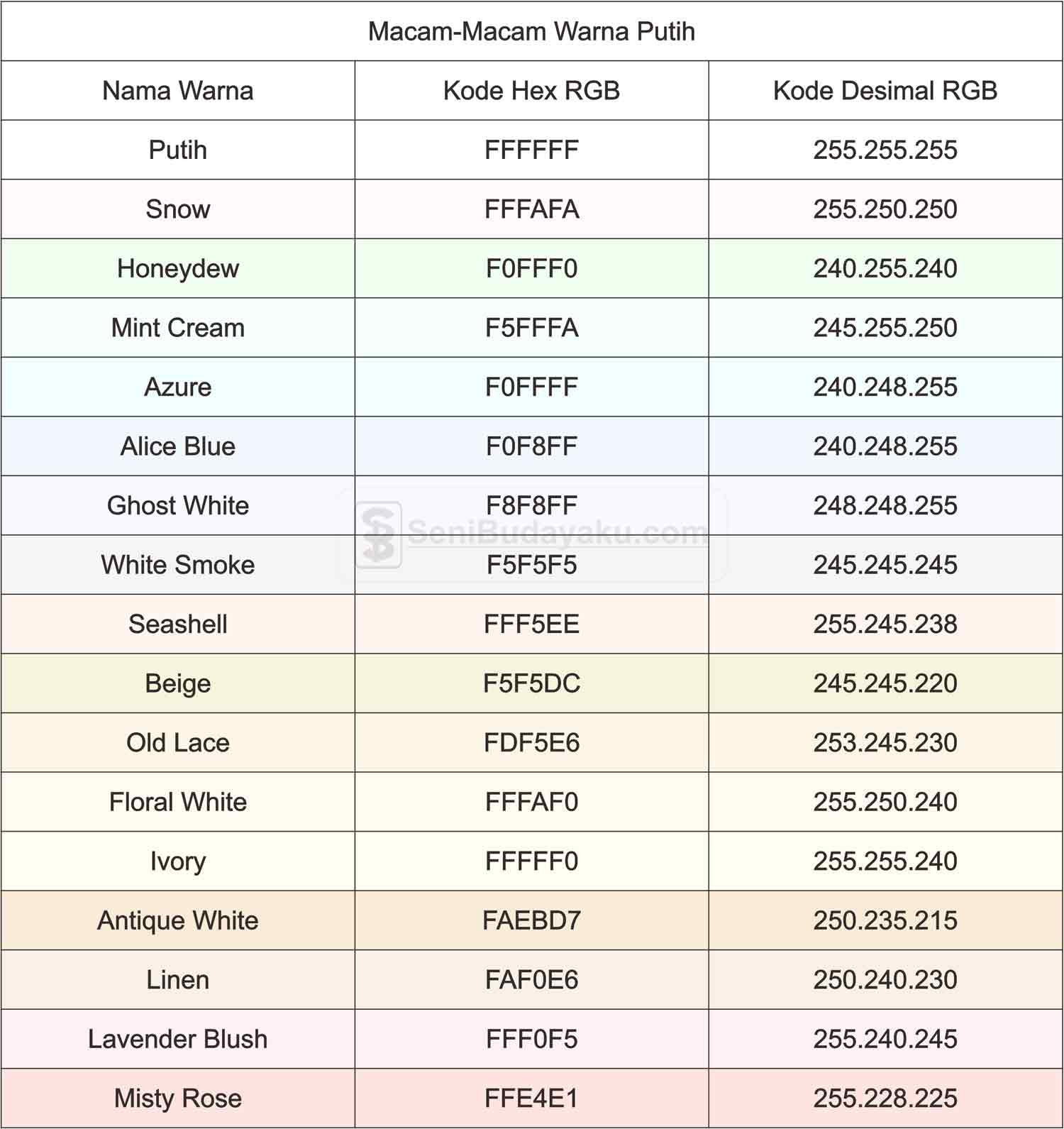
The precise shade of white can vary dramatically depending on the context. A pure white (#FFFFFF in hex) might appear stark and clinical in some situations, while a slightly warmer white might be more inviting. Understanding these nuances is crucial for web designers, graphic artists, and anyone working with digital color palettes.
Beyond the technical aspects, the cultural significance of white varies greatly across different societies. In Western cultures, white is often associated with purity, cleanliness, and innocence, while in some Eastern cultures, it can symbolize mourning or death. These cultural connotations play a role in how white is used in design and visual communication.
Historically, representing white digitally presented challenges due to limitations in early display technologies. As technology advanced, achieving accurate and consistent white across different devices became a key focus. This led to the development of standardized color spaces and coding systems.
The importance of white color codes lies in their ability to create a consistent visual experience across various digital platforms. Imagine a website where the background white appears differently on a phone compared to a laptop. This inconsistency can be jarring and unprofessional. Color codes ensure that the intended shade of white is displayed correctly regardless of the device.
One of the key issues associated with white color codes is accessibility. Individuals with visual impairments may struggle with stark white backgrounds, which can cause eye strain and reduce readability. Choosing appropriate shades of white and using sufficient contrast with text and other elements is crucial for creating accessible digital content.
A benefit of understanding white color codes is the ability to fine-tune the appearance of digital interfaces. For example, a web designer might use a slightly off-white background to create a softer, more inviting feel compared to a pure white.
Another benefit is ensuring brand consistency. By using specific white color codes in logos and branding materials, companies can maintain a cohesive visual identity across all platforms.
Lastly, precise control over white allows for better integration with other colors in a design. Subtle variations in white can enhance the vibrancy of surrounding colors and create a more harmonious overall aesthetic.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Precise White Color Control
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Consistent branding | Increased complexity for beginners |
| Improved accessibility | Potential for inconsistencies across devices if not managed correctly |
| Enhanced aesthetic control | Can be time-consuming to fine-tune for specific needs |
Best practices for using white color codes include considering accessibility guidelines, testing on different devices, and documenting chosen codes for consistency.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the hex code for pure white? (Answer: #FFFFFF)
2. How do I represent white in RGB? (Answer: (255, 255, 255))
3. Why does white sometimes look different on different screens? (Answer: Variations in display technology and calibration)
4. What are some accessible white color codes? (Answer: Slightly off-white shades can improve readability)
5. How can I choose the right white for my website? (Answer: Consider your brand, content, and target audience.)
6. Are there tools to help me select white color codes? (Answer: Yes, color pickers and palette generators are available.)
7. What is the role of white space in design? (Answer: White space improves readability and creates visual breathing room.)
8. How does white interact with other colors in a design? (Answer: White can enhance or mute surrounding colors depending on its shade and placement.)
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of white color codes is essential for anyone working with digital visuals. From web design and graphic art to user interface development, the seemingly simple choice of white plays a significant role in shaping the user experience. By paying attention to accessibility, brand consistency, and the subtle interplay of colors, you can harness the power of white to create effective and engaging digital experiences. Choosing the right shade of white can significantly impact readability, accessibility, and the overall aesthetic appeal of your digital content. By understanding the principles of color codes and best practices, you can create visually stunning and user-friendly designs that effectively communicate your message and enhance the user experience. Taking the time to carefully consider and implement these principles will ultimately lead to more effective and impactful digital communication.
Enhance your curb appeal with decorative concrete finishes
Level up your youtube presence crafting the perfect profile picture
Nfl week 7 predictions and expert insights