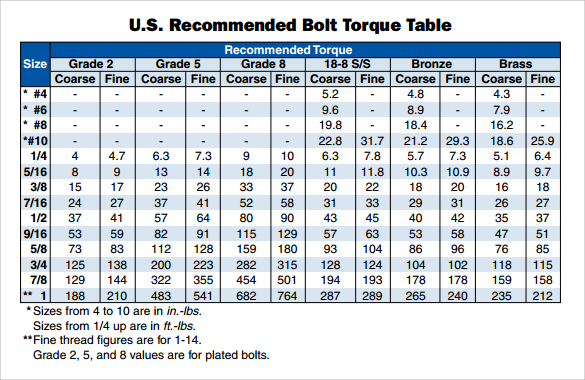
Ensuring a tight seal and structural integrity in industrial settings often hinges on the seemingly simple act of tightening bolts. But beneath the surface of this everyday task lies a world of specifications and standards, crucial for preventing leaks, failures, and potential disasters. This is where the ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) flange bolt torque specifications, often presented in handy chart form, become invaluable.
Imagine a massive pipeline transporting volatile materials, or a complex refinery operating under extreme pressures. The integrity of these systems depends heavily on properly torqued flange connections. Incorrectly tightened bolts can lead to leaks, compromising safety and potentially causing environmental damage. This is why understanding and applying the appropriate torque, as outlined in an ASME flange bolt torque reference, is paramount. These guidelines offer a standardized framework, ensuring consistent and reliable bolted joint assembly.
The need for standardization in flange bolt torquing led to the development of ASME standards. These standards, often compiled into user-friendly ASME flange bolt torque charts, provide engineers and technicians with the necessary information to achieve optimal bolt preload. This preload, the tension created within the bolt during tightening, is critical for creating a leak-proof seal and maintaining the structural integrity of the flanged connection. Without proper preload, flanges can separate, resulting in leaks or even catastrophic failures.
Finding the correct torque values can be a complex process, involving considerations like bolt size, material, and lubricant. An ASME flange bolt torque specification table simplifies this task by presenting the recommended values in a clear and concise format. These resources are typically available as PDFs, allowing for easy access and sharing. Using a reliable ASME flange bolt torque chart PDF ensures that bolting procedures adhere to industry-accepted best practices.
One of the key challenges in applying these standards lies in interpreting the information correctly. Different bolt materials, lubricants, and flange types require specific torque values. Misinterpreting these specifications can result in under- or over-torquing, both of which can compromise the joint’s integrity. Therefore, proper training and access to accurate, up-to-date ASME flange torque data are essential for anyone involved in bolted flange assembly.
The history of ASME flange bolt torque standards is intertwined with the development of pressure vessel and piping codes. As industries grew and the complexity of systems increased, the need for standardized bolting practices became evident. ASME took a leading role in developing these standards, ensuring consistent and reliable flange connections across various industries.
Benefits of using an ASME flange bolt torque guide include: 1) Preventing leaks and ensuring safety, 2) Achieving consistent bolt preload, and 3) Prolonging the life of flange connections.
Best practices include: 1) Using calibrated torque wrenches, 2) Applying lubricant consistently, 3) Following a specific tightening sequence, 4) Verifying torque values after a set period, and 5) Consulting updated ASME standards.
Challenges include variations in bolt material properties and temperature effects. Solutions involve material testing and temperature compensation techniques.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using an ASME Flange Bolt Torque Chart
There isn't really a disadvantage to using a proper torque chart, other than perhaps the time involved in locating the correct values. The advantage far outweigh any perceived downside.
FAQs:
1. Where can I find an ASME flange bolt torque chart? - Search online or consult ASME publications.
2. What factors influence torque values? - Bolt size, material, and lubricant.
3. Why is lubrication important? - Reduces friction and ensures consistent preload.
4. How often should torque wrenches be calibrated? - Regularly, as per manufacturer recommendations.
5. What is the importance of a tightening sequence? - Ensures even pressure distribution across the flange.
6. What are the consequences of over-torquing? - Bolt failure or flange damage.
7. What are the consequences of under-torquing? - Leaks and joint separation.
8. Where can I get training on proper bolting techniques? - Various training organizations and ASME offer courses.
Tips and tricks: Keep your ASME flange bolt torque charts updated. Use a torque wrench that’s appropriate for the bolt size. Clean and lubricate threads before assembly.
In conclusion, understanding and applying ASME flange bolt torque specifications is paramount for maintaining safety, preventing leaks, and ensuring the longevity of industrial systems. Using accurate ASME flange bolt torque charts, following best practices, and staying informed about the latest standards are crucial steps in achieving reliable bolted joint assembly. Investing in proper training and resources can significantly minimize the risks associated with improper bolting and contribute to a safer and more efficient operational environment. By prioritizing the correct application of torque specifications, industries can safeguard their operations and protect their valuable assets. Properly torqued flanges are the foundation of secure and reliable industrial systems, and understanding this fundamental principle is essential for anyone working with flanged connections. Make sure you prioritize correct torquing procedures – it's an investment in safety and reliability that pays off in the long run.
Level up your celebrations the galaxy of star wars cake design
That grinding noise when you turn understanding metal rubbing sounds
A toast to modern times exploring englands drinking culture