Are you tired of dealing with loose bolts or worse, catastrophic bolt failures? Understanding and applying the correct torque specifications for your fasteners, especially high-strength grade 8.8 bolts, is crucial for achieving secure and reliable assemblies. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of grade 8.8 bolt torque specs, equipping you with the knowledge and practical advice you need to ensure your bolted connections withstand the test of time and stress.
Tightening bolts might seem straightforward, but improper torque can lead to a range of issues, from joint loosening and vibration to severe component damage and safety hazards. Think of it like Goldilocks and the three bears – too little torque, and the joint will be weak; too much torque, and you risk stripping the threads or even fracturing the bolt. Finding that "just right" torque specification for your grade 8.8 bolts is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Torque specifications for grade 8.8 bolts are not arbitrary numbers pulled out of thin air. They are carefully calculated based on factors like the bolt's material properties (tensile strength, yield strength), the size of the bolt (diameter), and the intended application. These specifications are designed to achieve the ideal clamping force, which is the force holding the joined components together, preventing movement and maintaining the integrity of the assembly.
While standardized torque charts offer a starting point, various factors can influence the final torque value you should use. Lubrication, surface finish, and even temperature can affect the friction between the bolt and nut, impacting the achieved clamping force. Therefore, understanding these influencing factors and adjusting your tightening strategy accordingly is crucial for achieving consistent and reliable results.
Throughout this guide, we'll explore the nuances of grade 8.8 bolt tightening techniques, from basic principles to advanced best practices. We'll cover the importance of torque charts, the role of lubrication, and how to tackle common challenges like over-torquing and under-torquing. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or a DIY enthusiast, this article will empower you to confidently tighten grade 8.8 bolts and achieve secure, long-lasting connections.
The history of standardized torque specifications goes hand in hand with the development of high-strength fasteners like grade 8.8 bolts. As industries demanded stronger and more reliable connections, the need for precise tightening methods became evident. Early attempts at torque control were often rudimentary, relying on experience and feel. However, the advent of torque wrenches and standardized testing methods revolutionized the field, enabling engineers to specify and achieve consistent clamping forces.
Torque is a rotational force applied to a fastener, measured in units like Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lbs). For a grade 8.8 bolt, the torque specification dictates how much rotational force should be applied to achieve the desired clamping force. A simple example: imagine tightening a wheel lug nut. The torque specification ensures the wheel is securely attached to the axle without over-tightening and damaging the threads.
Benefits of proper torque specifications include: 1. Preventing Joint Failure: Correct torque prevents loosening and ensures the joint withstands operational stresses. 2. Enhanced Safety: Proper tightening minimizes the risk of component separation and potential accidents. 3. Increased Product Longevity: Accurate torque application reduces wear and tear, extending the life of the assembled components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Torque Specs for Grade 8.8 Bolts
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased reliability and safety | Requires specialized tools (torque wrenches) |
| Consistent clamping force | Can be time-consuming for large assemblies |
| Reduced risk of joint failure | Susceptible to errors if lubrication or surface conditions are not considered |
Best Practices: 1. Use calibrated torque wrenches. 2. Consult manufacturer's specifications. 3. Apply lubricant appropriately. 4. Tighten in a staged sequence for multi-bolt joints. 5. Verify torque after assembly.
Real Examples: 1. Automotive engine assembly. 2. Construction of steel structures. 3. Assembly of heavy machinery. 4. Installation of wind turbines. 5. Aerospace applications.
Challenges and Solutions: 1. Over-torquing: Solution: Use a calibrated torque wrench and follow specified values. 2. Under-torquing: Solution: Verify torque with a calibrated torque wrench. 3. Inconsistent torque: Solution: Use consistent lubrication and tightening techniques. 4. Damaged threads: Solution: Inspect bolts before use and avoid cross-threading. 5. Environmental factors: Solution: Consider temperature and humidity effects.
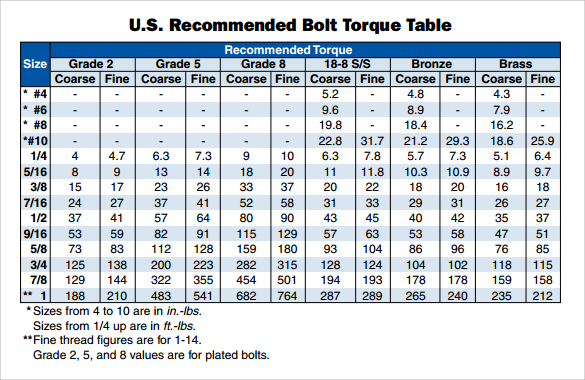
FAQ: 1. What is the torque spec for an M10 grade 8.8 bolt? A: Consult a torque chart for specific values. 2. Can I reuse grade 8.8 bolts? A: It depends on the application and condition of the bolt. 3. What is the difference between grade 8.8 and grade 10.9 bolts? A: Grade 10.9 bolts have higher tensile strength. 4. How does lubrication affect torque? A: Lubrication reduces friction, requiring lower torque for the same clamping force. 5. What is a torque wrench? A: A tool designed to accurately apply a specific torque. 6. Why is proper torque important? A: It ensures joint integrity and safety. 7. How do I choose the right torque wrench? A: Consider the required torque range and the accuracy needed. 8. Where can I find a torque chart for grade 8.8 bolts? A: Consult engineering handbooks or manufacturer's documentation.
Tips and Tricks: Clean the bolt threads and nut faces before assembly. Use a torque angle meter for critical applications. Regularly calibrate your torque wrenches. Refer to a reliable torque chart for grade 8.8 bolts based on size and lubrication conditions.
In conclusion, mastering torque specifications for grade 8.8 bolts is fundamental to achieving reliable and safe bolted connections. From preventing catastrophic failures to ensuring optimal performance, proper torque application plays a vital role in a wide range of industries. By understanding the principles of torque, utilizing calibrated tools, and adhering to best practices, you can confidently tighten grade 8.8 bolts and ensure the long-term integrity of your assemblies. Taking the time to learn and apply proper torque techniques will save you time, money, and potentially prevent serious safety hazards in the long run. Start implementing these strategies today and experience the benefits of secure and dependable bolted connections. Invest in a good quality torque wrench and familiarize yourself with reliable torque charts for grade 8.8 bolts. Your future self will thank you.
Remembering mary louise miller a life celebrated
Exploring the charm of sherwin williams fancy pink
A good wife foundation of a happy home