Ever wondered about the magic behind securely fastened structures, from skyscrapers to bicycles? It's not magic, it's engineering, and a critical part of that is understanding proper bolt tightening. This brings us to the essential tool: the metric bolt size torque chart.
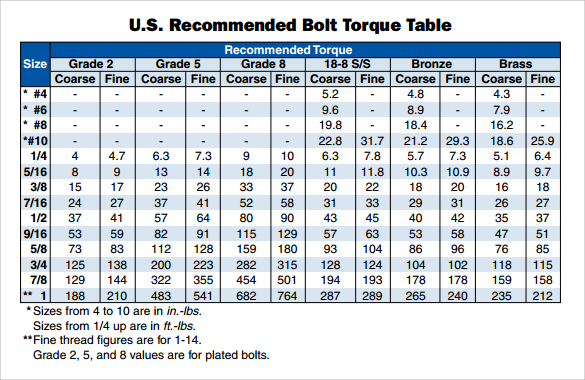
A metric bolt size torque chart is essentially a roadmap for achieving the correct tightness for your bolted connections. It provides recommended torque values based on the bolt's size and grade. This seemingly simple chart is a cornerstone of safe and reliable assembly across countless industries. Ignoring it can lead to anything from loose connections and vibrations to catastrophic failures.
Why metric? The metric system is the globally recognized standard for measurement, ensuring consistency and interoperability in engineering projects worldwide. Metric bolt sizes and torque specifications are integral to this standardized approach, facilitating clear communication and reducing the risk of errors.
The history of standardized torque charts goes hand-in-hand with the rise of mass production and interchangeable parts. As manufacturing became more complex, the need for precise and consistent fastening became paramount. Torque charts emerged as a solution, providing a reliable way to ensure uniform bolt tightening, regardless of who was performing the task.
One of the main issues related to metric bolt torque charts is the potential for misinterpretation or incorrect application. Using the wrong chart, misreading values, or failing to account for factors like lubrication can lead to under- or over-tightening. Both can have serious consequences. Under-tightening can result in loosening and joint failure, while over-tightening can damage the bolt, the fastened materials, or both.
A metric bolt is identified by its diameter and pitch, measured in millimeters. The grade of the bolt indicates its tensile strength. A torque chart cross-references these factors to provide the appropriate torque value, usually measured in Newton-meters (Nm). For example, an M8 bolt of a specific grade might require a torque of 25 Nm.
Utilizing a correct metric bolt torque specification offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it ensures the integrity and safety of the assembled structure. Properly torqued bolts create a strong and reliable connection, minimizing the risk of failure. Secondly, it prevents damage to the components. Applying the correct torque avoids stripping threads or damaging the materials being fastened. Finally, using a standardized torque chart contributes to consistency and quality in manufacturing processes.
Implementing metric bolt torque specifications effectively involves selecting the correct chart for the specific bolt and material, using calibrated torque wrenches, and following established procedures. Regularly checking and recalibrating torque wrenches is essential to maintain accuracy.
Before tightening any bolt, verify you have the correct metric bolt size torque chart, a calibrated torque wrench, and the correct bolt size and grade for the application. Clean the threads and apply the appropriate lubricant if specified. Tighten the bolt gradually and smoothly to the specified torque value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Metric Bolt Torque Chart
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ensures proper bolt tightening | Requires accurate charts and tools |
| Increases safety and reliability | Can be complex for non-standard applications |
| Prevents damage to components | Different materials and coatings can affect torque values |
Best Practices:
1. Always use a calibrated torque wrench.
2. Consult the correct chart for your specific bolt and material.
3. Clean and lubricate threads as needed.
4. Tighten bolts gradually and smoothly.
5. Regularly inspect and recalibrate torque wrenches.
FAQs:
1. What is torque? Torque is a twisting force that tends to cause rotation.
2. Why is proper torque important? Proper torque ensures a secure and reliable connection.
3. What is a torque wrench? A torque wrench is a tool designed to apply a specific amount of torque.
4. Where can I find a metric bolt size torque chart? Reliable charts are available from fastener manufacturers and engineering handbooks.
5. What factors influence torque values? Bolt size, grade, material, and lubrication all play a role.
6. What happens if I over-tighten a bolt? Over-tightening can damage the bolt, threads, or the materials being fastened.
7. What happens if I under-tighten a bolt? Under-tightening can lead to loosening and joint failure.
8. How often should I calibrate my torque wrench? Calibration frequency depends on usage, but annual calibration is generally recommended.
Tips and Tricks: When in doubt, consult an engineering reference or a qualified professional. Never guess at torque values.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing metric bolt size torque charts is fundamental to ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of any assembled structure. From preventing catastrophic failures to maintaining product quality, the importance of proper bolt tightening cannot be overstated. By following best practices, utilizing the correct tools, and consistently referencing accurate charts, we can achieve secure and dependable fastened connections across a wide range of applications. Investing time in understanding and applying this crucial aspect of engineering will ultimately save time, resources, and potentially prevent serious incidents. Remember to always prioritize safety and accuracy when working with bolted connections. Properly torqued bolts are the silent guardians of countless structures, ensuring their integrity and contributing to a safer and more reliable world. Take the time to understand your fasteners and torque requirements – it’s an investment that pays dividends in the long run.
Maizy chens last chance a culinary journey you wont forget
Navigating the dynamics of childhood friend romances chapter 15
Unlocking the emotional power of the boo and sully hug gif