Ever stripped a screw in aluminum? It's a frustrating experience, often leading to costly repairs or even component replacement. This common issue highlights the importance of understanding and applying the correct torque specifications when working with this lightweight metal. Getting it right isn't just about tightening a fastener – it’s about achieving a secure and reliable joint that can withstand the intended stresses and strains.
Aluminum's inherent properties, such as its lower tensile strength and softer nature compared to steel, necessitate a more nuanced approach to fastening. Over-tightening can easily strip threads or even damage the component itself, while under-tightening can result in loosening and eventual failure. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of torque specifications for aluminum, providing you with the knowledge and tools to avoid common pitfalls and achieve successful assemblies.
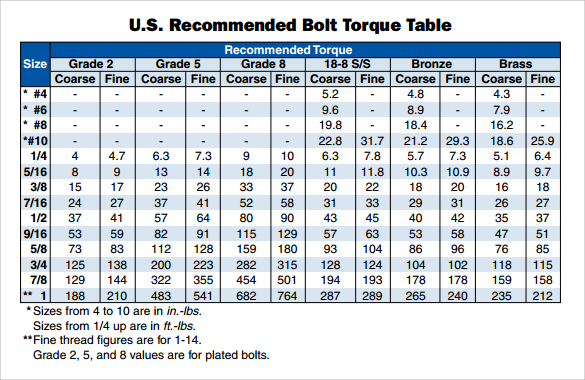
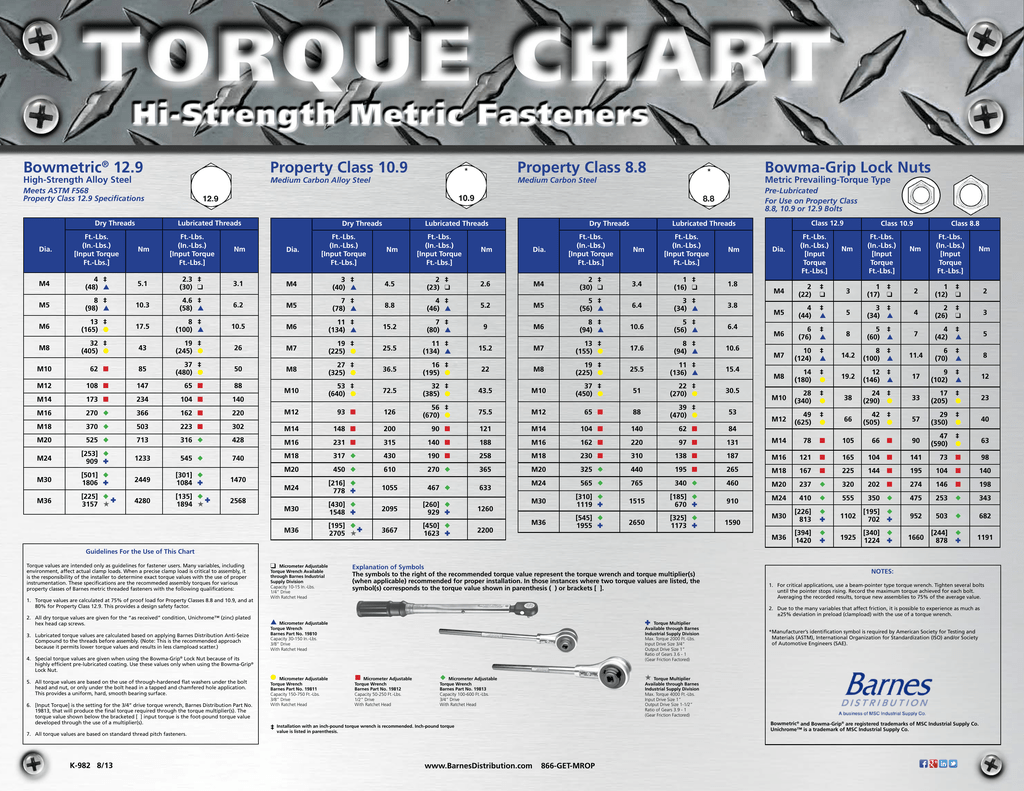
While the concept of torque itself isn’t specific to aluminum, its application to this metal requires careful consideration. Torque, a rotational force, is measured in units like Newton-meters (Nm) or pound-feet (lb-ft). Applying the appropriate torque value ensures that the fastener is tightened just enough to create a secure clamp load without exceeding the material’s limits. The correct torque spec for aluminum depends on various factors, including the fastener size, thread pitch, material, and lubricant used.
Historically, determining the correct torque for aluminum often relied on trial and error, leading to inconsistencies and potential failures. As aluminum became more prevalent in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction, the need for standardized torque values became critical. Today, engineers and manufacturers rely on extensive testing and data analysis to establish reliable torque specifications for different aluminum alloys and fastener types. This information is readily available in engineering handbooks, manufacturer specifications, and online resources.
The importance of proper torque specification application to aluminum cannot be overstated. In critical applications, such as aircraft assembly or engine construction, incorrect torque can have catastrophic consequences. Even in less critical scenarios, like assembling furniture or electronic devices, proper torque ensures the longevity and reliability of the product. Understanding and applying correct tightening techniques translates directly to stronger, safer, and more durable aluminum assemblies.
One significant challenge when working with aluminum is its susceptibility to galvanic corrosion, particularly when dissimilar metals are involved. Using anti-seize lubricants can help mitigate this issue, but it’s essential to adjust the torque value accordingly, as lubricants can affect the clamping force achieved. Additionally, the ductility of aluminum means that it can deform under pressure, making it more prone to thread stripping. This highlights the need for careful control of the applied torque.
Three key benefits arise from correct aluminum torque specifications. First, proper torque ensures joint integrity, preventing loosening or failure under stress. Second, it minimizes the risk of damaging the aluminum component through over-tightening. Finally, using the correct torque contributes to the overall durability and longevity of the assembly.
Best practices for working with aluminum include using the correct tools, such as calibrated torque wrenches, and following manufacturer recommendations. Cleaning threads before assembly and applying the appropriate lubricant are also crucial steps.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Specifying Torque for Aluminum
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased joint reliability | Potential for over-tightening |
| Reduced risk of thread stripping | Need for calibrated tools |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is torque? - Torque is a rotational force.
2. Why are torque specs important for aluminum? - They prevent damage and ensure proper joint integrity.
3. Where can I find torque specifications? - In manufacturer manuals or engineering handbooks.
4. What tools do I need? - A calibrated torque wrench.
5. What are the consequences of over-tightening? - Thread stripping or component damage.
6. What are the consequences of under-tightening? - Joint loosening and potential failure.
7. How do lubricants affect torque? - Lubricants can reduce friction, requiring torque adjustments.
8. What is galvanic corrosion? - Corrosion that occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact.
In conclusion, understanding and applying correct torque specifications to aluminum is fundamental for creating strong, reliable, and long-lasting assemblies. From aerospace components to everyday household items, the principles of proper torque application remain crucial. By considering the unique properties of aluminum, utilizing the right tools, and adhering to best practices, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure the integrity of your aluminum projects. Take the time to consult manufacturer guidelines, invest in quality tools, and practice proper techniques. The benefits of correctly torqued aluminum components, from increased safety to enhanced product durability, far outweigh the effort invested in mastering this essential skill. By prioritizing accurate torque application, you ensure the success and longevity of your aluminum projects.
Conquering the road your guide to a used toyota sequoia trd
Level up your game bowling dynamics pro shop phoenix
Missouri city tx power outage map your guide to staying informed