Ever wondered how federal government employees are paid? It's a complex system, but at its heart lies the OPM General Schedule (GS) rate table. This comprehensive pay scale governs the salaries of the vast majority of civilian federal workers, impacting everything from entry-level positions to senior executives. Understanding this system is crucial not only for those considering or currently working in federal service but also for anyone interested in how taxpayer dollars are allocated.
The GS pay scale isn't just a list of numbers; it's a framework that ensures fair and consistent compensation across different government agencies and roles. It takes into account factors like job complexity, required skills, and geographic location to determine appropriate salary levels. This structure provides transparency and helps to attract and retain qualified individuals in public service.
The origins of the GS pay system can be traced back to the Classification Act of 1923, which sought to standardize federal positions and salaries. Over the years, the system has evolved, reflecting changes in the workforce and the economy. Today, the OPM (Office of Personnel Management) manages the GS pay scale, regularly updating it to ensure it remains competitive and equitable. One of the main issues surrounding the GS pay scale is maintaining a balance between attracting and retaining talent while also managing federal budget constraints. This requires careful consideration of economic factors, pay comparability with the private sector, and the specific needs of the government workforce.
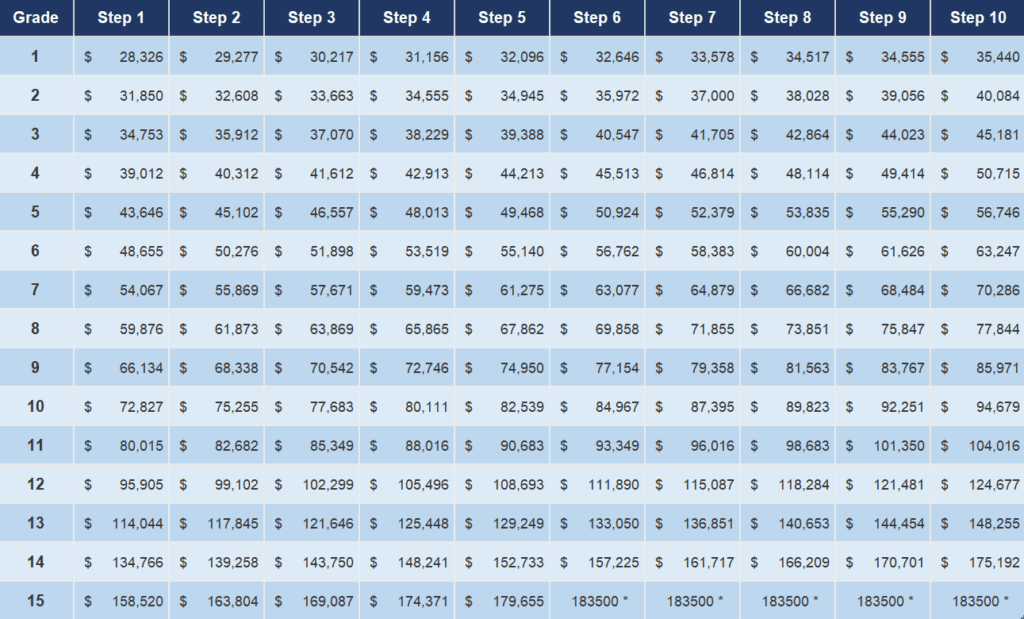
The GS pay scale is structured around a series of numbered grades, ranging from GS-1 (entry-level) to GS-15 (senior executive). Within each grade, there are ten steps, representing incremental increases in salary based on experience and performance. Locality pay adjustments are also factored in, recognizing the varying cost of living across different geographic areas. For instance, a GS-9 employee in New York City will typically earn a higher salary than a GS-9 employee in a smaller, less expensive city.
The GS schedule has a profound impact on the federal workforce. It provides a clear career progression path, motivating employees to develop their skills and advance within the government. It also ensures that federal salaries remain competitive with the private sector, helping to attract and retain highly qualified individuals. Furthermore, the transparency of the system builds public trust by demonstrating a fair and consistent approach to compensating federal employees.
Understanding how the OPM GS rate information impacts your potential earnings is essential if you're considering a federal career. You can find detailed GS rate tables on the OPM website, providing a breakdown of salaries for each grade and step, along with locality pay adjustments for different regions.
A simplified example: A GS-7, Step 1 employee in the "Rest of U.S." locality pay area might earn $43,615 annually (based on 2023 rates). As they gain experience and progress to higher steps within GS-7, their salary will increase accordingly. If they were located in a higher-cost area like San Francisco, their salary would be adjusted upwards to reflect the local cost of living.
Benefits of the OPM GS system include transparency, standardized pay, and career progression opportunities. It offers a structured path for advancement, encouraging employee growth and development. The clearly defined salary ranges provide a sense of stability and predictability, making it easier for individuals to plan their finances.
One crucial aspect of navigating the GS pay scale is understanding locality pay. This adjustment ensures that federal employees in higher-cost areas receive salaries commensurate with their local expenses. The OPM website provides detailed locality pay tables, enabling you to determine the adjusted salary for your specific location.
Challenges related to the OPM GS rate table might include staying up-to-date with the latest changes and understanding the complexities of locality pay. Solutions include regularly checking the OPM website for updates and using online salary calculators to estimate your potential earnings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the OPM GS Rate Table
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and standardization | Can be inflexible for specialized roles |
| Clear career progression path | Pay may not always be competitive with private sector for certain positions |
FAQ: How often is the GS pay scale updated? Generally, the GS pay scale is adjusted annually.
FAQ: What is locality pay? Locality pay is an adjustment to the base GS salary based on the cost of living in a specific geographic area.
One tip for maximizing your earnings under the GS system is to understand the performance appraisal process. Strong performance evaluations can lead to faster progression through the steps within your grade, resulting in higher salaries.
In conclusion, the OPM GS rate table is the cornerstone of federal employee compensation. It provides a structured, transparent, and equitable system for determining salaries, impacting the lives of hundreds of thousands of public servants. Understanding the nuances of this system, including grades, steps, and locality pay, is essential for anyone navigating the federal workforce. By staying informed about the GS pay scale and its regular updates, you can make informed decisions about your career and financial future. Whether you're a current federal employee, a prospective applicant, or simply interested in how the government compensates its workforce, familiarizing yourself with the OPM GS rate information is a valuable endeavor.
Find fedex shipping centers near you
Boat trailer light installation guide
Finding serenity with warm blue gray paint