Are you approaching 65 or already there and feeling overwhelmed by the complexities of Medicare? You're not alone. Millions of Americans face the same challenge each year. This guide is designed to demystify Medicare and Medicare Supplement Insurance, providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Medicare, the federal health insurance program for individuals 65 and older and certain younger individuals with disabilities, can be a confusing landscape to navigate. From Original Medicare (Parts A and B) to Medicare Advantage (Part C) and Medicare Part D (prescription drug coverage), the options can feel overwhelming. Adding to the complexity is the consideration of Medicare Supplement Insurance, also known as Medigap, which helps cover some of the out-of-pocket costs Original Medicare doesn't cover.
Understanding the different parts of Medicare is crucial. Part A covers hospital insurance, while Part B covers medical insurance, such as doctor visits and outpatient care. Part D provides prescription drug coverage. Medicare Advantage plans, offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare, typically combine Parts A, B, and often D into a single plan. This can simplify billing, but it also often restricts your choice of doctors and hospitals to those within the plan's network.
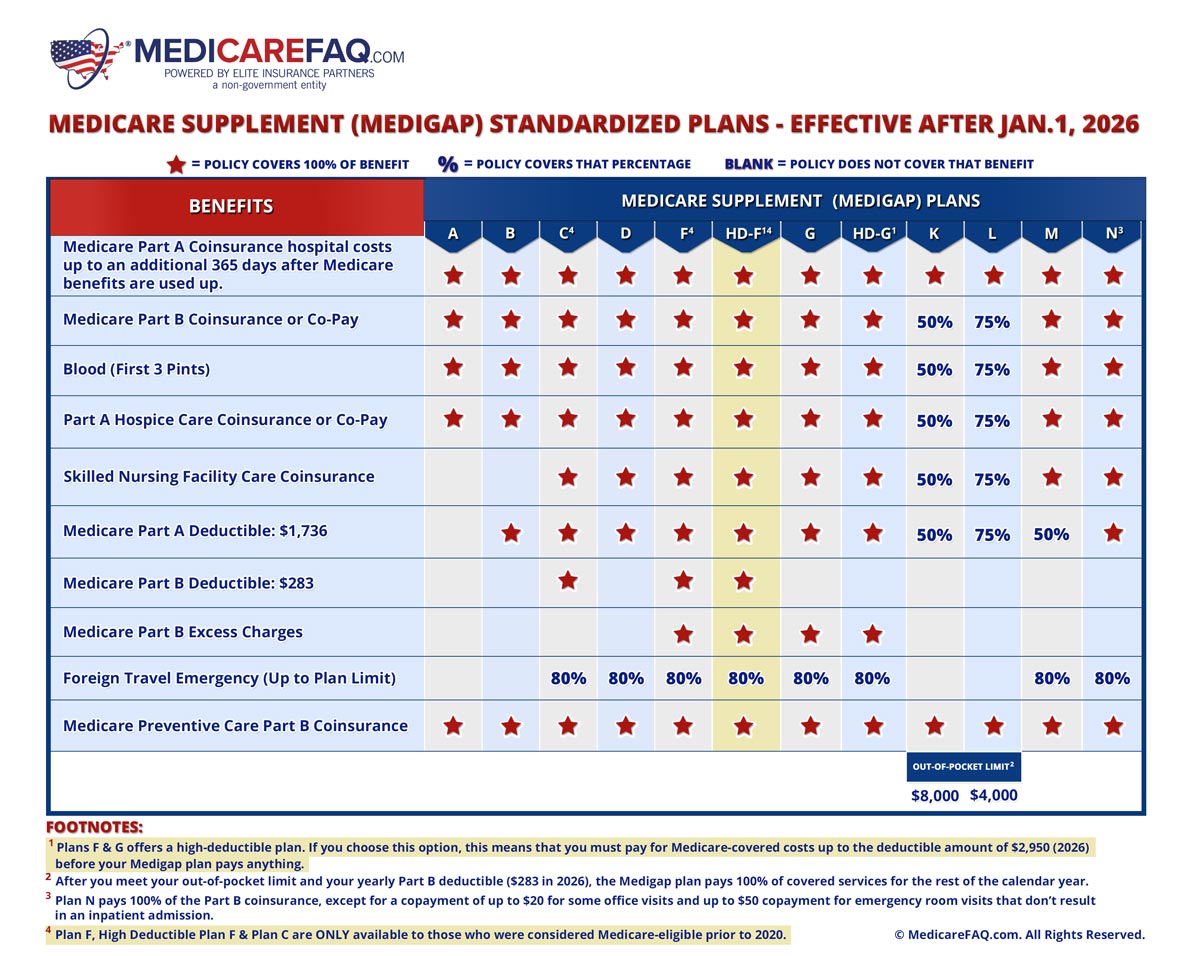
Medicare Supplement Insurance plans, offered by private insurance companies, are designed to work alongside Original Medicare (Parts A and B). They help pay for some of the out-of-pocket expenses that Original Medicare doesn't cover, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. Choosing the right Medigap policy can provide significant financial peace of mind, protecting you from unexpected medical expenses.
To begin your journey through the Medicare maze, it's important to understand your eligibility and enrollment periods. Generally, you become eligible for Medicare three months before your 65th birthday, the month of your 65th birthday, and three months after. Missing this Initial Enrollment Period can lead to penalties and delays in coverage, so careful planning is essential.
Medicare has its roots in the Social Security Amendments of 1965, signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. Its creation was a landmark achievement, addressing the growing healthcare needs of older Americans. Over time, Medicare has evolved to meet the changing needs of beneficiaries, adding prescription drug coverage and expanding options with Medicare Advantage plans.
A key issue surrounding Medicare is its long-term sustainability. With an aging population and rising healthcare costs, ensuring the program's solvency for future generations is a significant challenge.
One benefit of Medicare is its guaranteed issue provision, meaning you can't be denied coverage based on pre-existing conditions. Medicare Supplement Insurance also offers guaranteed issue during certain enrollment periods. This protection is particularly important for individuals with chronic health conditions.
Another advantage is the choice and flexibility offered by the various Medicare plans. You can choose Original Medicare with a supplement plan or opt for a Medicare Advantage plan, depending on your individual needs and preferences.
A third benefit is the portability of Medicare coverage. You can generally access healthcare services anywhere in the United States where Medicare is accepted. This is especially beneficial for individuals who travel frequently or split their time between multiple residences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Original Medicare with Supplement vs. Medicare Advantage
| Feature | Original Medicare + Supplement | Medicare Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Choice of Doctors/Hospitals | Generally, see any doctor/hospital that accepts Medicare | Limited network of doctors/hospitals |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Predictable with supplement plan | Can vary depending on plan and utilization |
| Coverage | Nationwide coverage | Generally limited to service area |
FAQ:
1. When can I enroll in Medicare? Generally, three months before, the month of, and three months after your 65th birthday.
2. What does Medicare Part B cover? Medical insurance, such as doctor visits and outpatient care.
3. What is Medicare Supplement Insurance? Supplemental insurance that helps pay out-of-pocket costs of Original Medicare.
4. What is the difference between Medicare Advantage and Original Medicare? Medicare Advantage combines Parts A, B, and often D, while Original Medicare allows more choice of doctors and hospitals.
5. How much does Medicare cost? Costs vary depending on the parts of Medicare you choose and your income.
6. How do I choose a Medicare Supplement plan? Consider your budget and desired level of coverage.
7. What is the Medicare donut hole? A coverage gap in Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage.
8. Where can I get more information about Medicare? Medicare.gov is a great resource.
Navigating the complexities of Medicare and Medicare Supplement Insurance is a crucial step in securing your healthcare future. By understanding the various components of Medicare, exploring your options, and making informed decisions, you can ensure you have the coverage you need to maintain your health and well-being. Taking the time to research and compare plans can save you money and provide peace of mind knowing you're prepared for any healthcare challenges that may arise. Remember to utilize available resources, such as Medicare.gov and your State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP), for personalized guidance. Don’t hesitate to seek advice from trusted professionals to ensure you make the best choices for your individual needs. Your health and financial security depend on it.
Black and white flame skull tattoos meaning designs inspiration
Suzys zoo baby shower extravaganza
Dell laptop screen flipped easy fixes