Imagine a one-way street for electricity. That's essentially what a diode is, and its symbol reflects this unique characteristic. Understanding this symbol is fundamental to reading and interpreting electronic circuits.
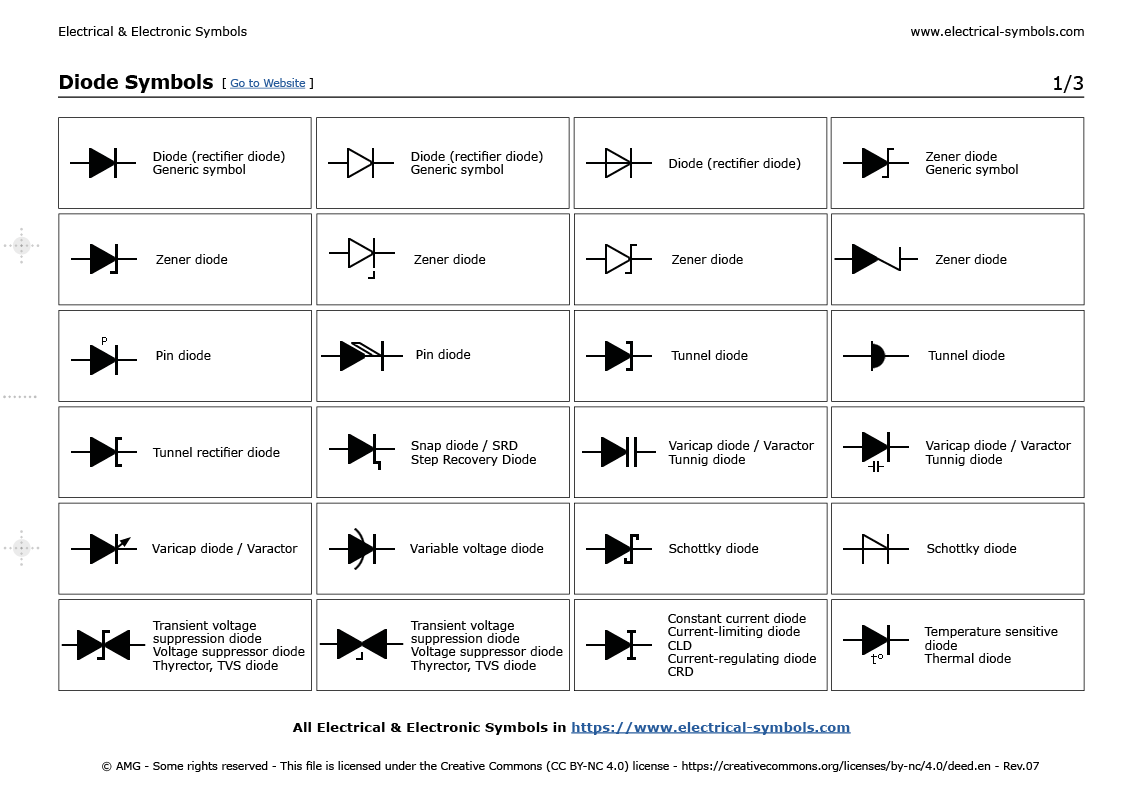
The diode symbol depicts an arrow meeting a vertical line. The arrow indicates the direction of conventional current flow, while the line acts as a barrier in the opposite direction. This simple representation encapsulates the diode's core function: allowing current to pass freely in one direction (forward bias) while blocking it in the reverse direction (reverse bias). Grasping the diode symbol is crucial for anyone working with electronics, from hobbyists to engineers.
Historically, the first diodes were vacuum tubes, followed by semiconductor diodes made from materials like selenium and germanium. Today, silicon is the most common material used in diode manufacturing. The diode symbol has evolved along with the technology, yet its core meaning remains unchanged. Recognizing this symbol allows us to quickly identify diodes in circuit diagrams and understand their role in the overall circuit functionality.
The importance of the diode symbol cannot be overstated. It's a universal language in electronics, enabling clear communication and understanding between designers, engineers, and technicians worldwide. Imagine trying to decipher a circuit without a standardized symbol for the diode – it would be chaotic and inefficient. The symbol's simplicity and clarity are essential for efficient circuit design and analysis.
One of the main issues related to understanding the diode symbol is associating it with the actual flow of electrons, which is opposite to conventional current flow. This can be confusing for beginners. Remember that the arrow in the symbol points in the direction of conventional current, which is the flow of positive charge. Electrons, however, flow in the opposite direction. Once this distinction is clear, interpreting the diode symbol becomes much easier.
Diodes are used in countless applications, from rectifying AC power to voltage regulation and signal demodulation. A simple example is a rectifier circuit, where diodes convert alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC). The diode symbol in such a circuit clearly shows how current is allowed to flow through the diode in only one direction, effectively blocking the negative half-cycles of the AC input.
Several benefits come with understanding the diode symbol. First, it simplifies circuit analysis, allowing you to quickly identify the function of a diode within a larger circuit. Second, it facilitates communication between engineers and technicians, ensuring everyone is on the same page. Third, it enables efficient troubleshooting, as recognizing the diode's role can quickly narrow down the source of a problem.
One practical example is using a diode to protect a sensitive electronic component from reverse voltage. The diode's symbol, placed correctly in the circuit diagram, clearly illustrates how it blocks any reverse current that could damage the component.
Another example is using diodes in logic circuits. Here, they can perform functions like AND or OR gates. The diode symbols in these logic circuits illustrate how the diodes control the flow of current, implementing the desired logic operation.
If you're working with circuits, learning the diode symbol is essential. A simple way to remember it is to think of the arrow as pointing in the direction of allowed current flow. Practice drawing the symbol and identifying it in various circuit diagrams.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Diodes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and inexpensive | Limited current and voltage handling capacity |
| Wide range of applications | Temperature sensitive |
Frequently Asked Questions about Diodes:
1. What is a diode? A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction.
2. What is the symbol for a diode? The diode symbol is an arrow pointing towards a vertical line.
3. What is the function of a diode? A diode allows current to flow in one direction (forward bias) and blocks current in the opposite direction (reverse bias).
4. What are the types of diodes? Common types include rectifier diodes, Zener diodes, LEDs, and Schottky diodes.
5. How do I test a diode? A multimeter can be used to test a diode by measuring its forward and reverse resistance.
6. What is forward bias? Forward bias is when a positive voltage is applied to the anode and a negative voltage to the cathode, allowing current to flow.
7. What is reverse bias? Reverse bias is when a negative voltage is applied to the anode and a positive voltage to the cathode, blocking current flow.
8. What are some applications of diodes? Diodes are used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, logic circuits, and signal processing applications.
In conclusion, the diode symbol is a fundamental element in electronics, representing a component with a unique and essential function. Understanding this symbol is crucial for anyone working with or studying electronic circuits. From its historical origins to its modern applications, the diode symbol plays a vital role in clear communication and efficient circuit design. The ability to interpret this symbol allows us to understand the flow of current, analyze circuits, and troubleshoot electronic systems effectively. By learning this simple yet powerful symbol, you unlock a deeper understanding of the world of electronics. Take the time to familiarize yourself with the diode symbol and its significance, and you'll find it an invaluable tool in your electronics journey.
Avon nc real estate your outer banks escape awaits
Exploring ann arbor a closer look at 2350 w stadium blvd
Ice age 4 continental drift cast a mammoth ensemble