Imagine a world without lungs. How would you breathe? Insects, the most diverse group of animals on Earth, have solved this challenge with an ingenious system: tracheal respiration. This intricate network of tubes, beautifully illustrated in a tracheal respiration diagram in insects, delivers oxygen directly to the tissues, bypassing the need for a circulatory system to transport gases.
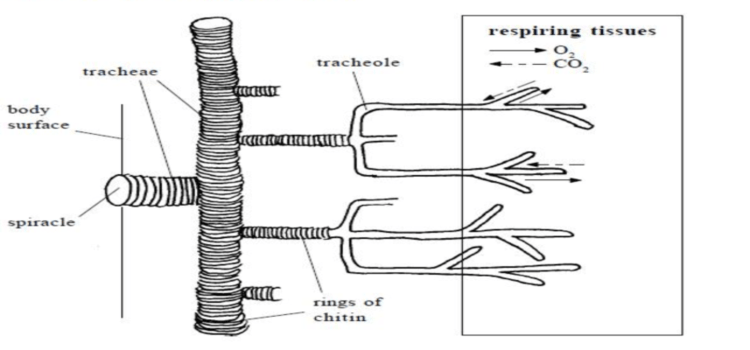
Understanding insect respiration starts with visualizing the tracheal respiration diagram. This schematic representation reveals a complex network of tubes, called tracheae, which branch throughout the insect's body. These tracheae begin as openings on the exoskeleton called spiracles and progressively divide into smaller tubes, the tracheoles, reaching individual cells. This direct delivery system is remarkably efficient, allowing insects to thrive in diverse environments.
The evolutionary history of insect tracheal respiration is a testament to its effectiveness. This system likely arose in early terrestrial arthropods as a solution to the challenges of obtaining oxygen from air. The development of the tracheal system, as depicted in a simplified tracheal system diagram, was a key innovation that facilitated the remarkable diversification and success of insects.
The importance of understanding insect respiration extends beyond basic biology. Knowledge of the tracheal system, as visualized in a detailed insect respiratory system diagram, has implications for pest control. Insecticides can target the spiracles, disrupting oxygen uptake and leading to insect mortality. This understanding allows for the development of more targeted and effective pest management strategies.
A key issue related to the tracheal system is water loss. While spiracles allow for gas exchange, they also provide a pathway for water to escape. Insects have evolved various mechanisms, including the ability to close their spiracles, to minimize water loss, particularly in arid environments. Studying the tracheal respiration process diagram helps us understand these adaptations.
A tracheal respiration in insects diagram typically shows the spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles. Spiracles are valve-like openings that regulate the flow of air into the tracheal system. Tracheae are the larger tubes that transport air throughout the body, while tracheoles are the finer branches that deliver oxygen directly to the cells. A simple example is the grasshopper, where you can observe the rhythmic opening and closing of the abdominal spiracles.
Benefits of studying a tracheal respiration diagram include: 1. Understanding insect physiology: The diagram provides a visual representation of how insects breathe, facilitating a deeper understanding of their biological processes. 2. Developing pest control strategies: Knowledge of the tracheal system can be used to develop more effective insecticides that target respiration. 3. Appreciating evolutionary adaptations: Studying the diagram reveals the ingenious solutions insects have evolved for gas exchange.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tracheal Respiration
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Efficient oxygen delivery directly to tissues | Limits body size due to diffusion constraints |
| No need for a separate circulatory system for gas transport | Potential for water loss through spiracles |
Frequently Asked Questions about Insect Tracheal Respiration:
1. How do insects breathe? Insects breathe using a network of tubes called tracheae.
2. What are spiracles? Spiracles are openings on the insect's exoskeleton that allow air to enter the tracheal system.
3. What are tracheoles? Tracheoles are the smallest branches of the tracheal system, delivering oxygen directly to cells.
4. How does the tracheal system differ from lungs? The tracheal system delivers oxygen directly to tissues, while lungs rely on a circulatory system.
5. How do insects control water loss through spiracles? Insects can close their spiracles to minimize water loss.
6. How is the tracheal system depicted in a diagram? A tracheal respiration diagram typically shows the spiracles, tracheae, and tracheoles.
7. What is the evolutionary significance of the tracheal system? It allowed insects to colonize land and diversify successfully.
8. How can knowledge of the tracheal system be used in pest control? Insecticides can be developed to target the spiracles and disrupt respiration.
In conclusion, the diagram of tracheal respiration in insects offers a crucial window into the fascinating world of insect physiology. Understanding this unique respiratory system, its evolutionary significance, and its implications for areas like pest control underscores the importance of studying these intricate diagrams. By appreciating the ingenious adaptations of insects, we gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the remarkable diversity of life on Earth. Further exploration of insect respiration can be found in entomology textbooks and online resources dedicated to insect physiology. Explore the microscopic world of insect breathing and discover the wonders of the tracheal system.
Hvac condensation pumps a comprehensive guide
Navigating marylands compensation landscape
Effortless tiktok birthday invitations